深度探索DxFramework 10-1
Table of Contents
请尊重原作者的工作,转载时请务必注明转载自:www.xionggf.com
第10章 进入三维的世界 1
10.1.3D预备数学知识和相关代码的分析
10.2 向量,矩阵,四元数
10.3 三维几何工具集
10.3.1 与三维空间的平面相关算法
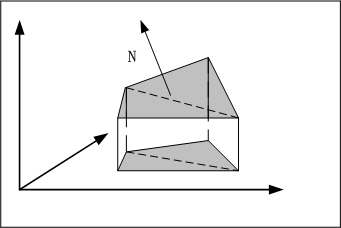
对于给定的3D点P0和法向量N,过点P0并且和N垂直的平面就可以定义为满足方程N.(P-P0) = 0的集合。(不明白这个定义怎么来的读者,可以回忆一下两向量点积的几何意义)。如下图,平面中任意点与P0的连线都与法线N是垂直的。
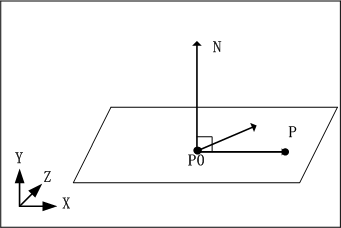
如果令法向量N为(A,B,C),点P0为(P0x,P0y,P0z)。则平面的方程为:
$ Ax + By + Cz + D = 0 $ ( 此时 $ Ax + By +Cz + D = \overset{\rightharpoonup}{N}\cdot P $ ,$ D = -\overset{\rightharpoonup}{N}\cdot P $ )
根据平面法线的指向,平面把它所处的空间划分成两个半空间,法线所指向的半空间称为正半空间,也可以称为正侧空间。另一半则称为负半空间,也称为负侧空间。判断某点和某平面的位置关系可以依照上面三个判断式,如下:
| 判断式 | 位置关系 | |
|---|---|---|
| Ax+By+Cz+D=0 | 点(x,y,z)在平面上 | |
| Ax+By+Cz+D>0 | 点(x,y,z)在正半空间 | |
| Ax+By+Cz+D<0 | 点(x,y,z)在负半空间 |
在此可以举一个例子来说明。如下图:
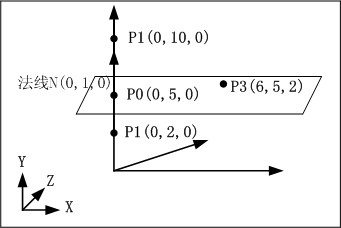
在图中,平面A由法线N(0,1,0)和点P0(0,5,0)定义。那么,定义式Ax+By+Cz+D=0的D为: D=-N.P0 = -(00+15+0*0) = -5
P3的坐标为(6,5,2),代入方程式Ax+By+Cz+D中,为: 60+51+0*2-5=0
所以P3在平面上。P1的坐标为(0,10,0),代入方程式Ax+By+Cz+D中,为: 00+101+0*0-5=5>0
所以P1在平面的正半空间。P2的坐标为(0,2,0),代入方程式Ax+By+Cz+D中,为: 00+21+0*0-5=-3<0
所以P1在平面的负半空间。tool3d.cpp文件中定义了点和平面的位置关系判断的两个函数,如下:
//检查某点p_Point是否在某平面p_Plane的正侧:
bool positiveSide(D3DXVECTOR3* p_Point, D3DXPLANE* p_Plane)
{
return p_Plane->a * p_Point->x + p_Plane->b * p_Point->y +
p_Plane->c * p_Point->z + p_Plane->d > 0;
}
//检查某点p_Point和某平面p_Plane的位置关系,1为正侧,
//-1为负侧,0为点在平面上
int whichSide(D3DXVECTOR3* p_Point, D3DXPLANE* p_Plane)
{
float temp = p_Plane->a * p_Point->x +
p_Plane->b * p_Point->y +
p_Plane->c * p_Point->z + p_Plane->d;
if (temp > epsilon)
{
return 1;
}
else if (temp < (-epsilon))
{
return -1;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
10.3.2 计算三角形面积和凸多边形面积
计算三角形的面积的方法有多种,最常用的就是把两个全等的三角形,组合成一个平行四边形,然后求出平行四边形的面积再除以2就可以了。当给定一个三角形的三个顶点坐标的时候,利用向量叉积的几何性质,就可以按照上述方法来求出三角形的面积。我们知道,两向量P×Q,有|P×Q| = |P|.|Q|.sinA,A是两向量的夹角。从几何意义上来说,两向量的叉积的模,就等于以这两向量的模的长度为不等边,组成的平行四边形的面积,如下图:
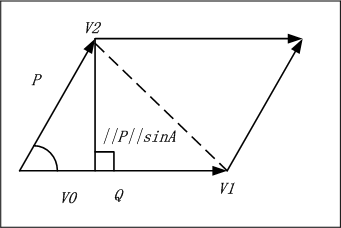
DXFrameWork提供了计算三角形面积的函数,如下:
XFLOAT triangleArea(D3DXVECTOR3* p0, D3DXVECTOR3* p1,
D3DXVECTOR3* p2)
{
D3DXVECTOR3 v1 = (*p1) - (*p0);
D3DXVECTOR3 v2 = (*p2) - (*p0);
return 0.5 * D3DXVec3Length(D3DXVec3Cross(&v1, &v1, &v2));
}
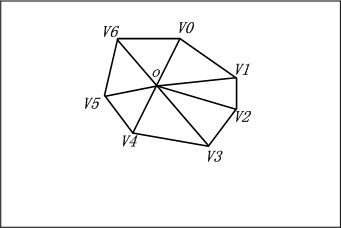
知道了三角形的面积如何计算,接下来凸多边形的面积也好计算了。无非就是把凸多边形分解为若干个三角形,计算每个三角形的面积后累加即可。
//第一个参数是凸多边形的顶点列表,第二个参数numPoints是凸多边形的顶点数
XFLOAT convexPolygonArea(D3DXVECTOR3* points, int numPoints)
{
int i;
XFLOAT sum = 0.0;
//注意points[0]是该凸多边形分解而成的三角形的共用顶点
for (i = 2; i < numPoints; i++)
{
sum += triangleArea(&points[0],&points[i - 1],&points[i]);
}
return sum;
}
计算凸多边形的面积的示意图如下:
10.3.3 线段和面(face)相交检测
检查某线段是否和某面(face,注意不是平面)相交的代码如下:
bool checkEdgeIntersectsFace( D3DXVECTOR3 p_Edge[2], D3DXVECTOR3* p_Face, int numVertices, D3DXPLANE* p_Plane, D3DXVECTOR3* p_PointOnPlane) {
//要进行相交判断的face,只能是三角形或者是四边形。
if(numVertices > MAX_VERTICES_FOR_EDGE_INTERSECT_CHECKING)
{
throw Error(_T("checkEdgeIntersectsFace : Number of
vertices used in checking an edge
intersects with a face is too many"));
return false;
}
// 通过计算面积,判断要检查的face是不是一个一维的线段。如果是就返回false
XFLOAT area = convexPolygonArea(p_Face, numVertices);
if ((area < 0.001) && (area > -0.001))
return false;
//如果线段的两个端点都在face所处平面的同一侧,则显然这个线段是不会和该face相交的
bool temp1, temp2;
temp1 = positiveSide(&p_Edge[0], p_Plane);
temp2 = positiveSide(&p_Edge[1], p_Plane);
if (temp1 == temp2)
{
return false;
}
//再检查线段和face所在的平面是否相交,如果不相交,则线段肯定不和face相交
if (D3DXPlaneIntersectLine(p_PointOnPlane, p_Plane, &p_Edge[0], &p_Edge[1]) == NULL)
{
return false;
}
如果计算到线段和face所在的平面相交,那么接下来就是要判断相交点是落在face的内侧还是外测了。在计算机图形学中,往往把三维对象通过降维处理,可以降低问题的复杂度。降维的方法是:通过去掉face的法线N的绝对值最大的分量所对应的坐标,就可以把问题降到二维空间来考虑。如下图所示,降维过程相当于把face投影到xy,xz或者是yz平面上。在此先假设被去掉的是z坐标,即投影到xy平面上。如下图投影多边形到XZ,YZ,XY平面上
判断某点在不在多边形内,可以把问题转化为判断点在不在某三角形内。如上图,把多边形划分为若干个三角形。然后判断点是否在这些三角形内,只要判断到点在某一三角形内,就肯定这点在此多边形内。先考虑如何判断点是否在三角形内。上面已经把三角形投影到一个二维平面来进行考虑。假定投影在了xz平面上。对三角形的每条边进行下面的二维差运算,有:
E = P1-P0
F=P2-P0
G=P-P0
从本质上说,这样做的意义上移动坐标系,使得顶点P0位于原点位置。或者可以认为是以P0为原点。如下图所示。

在上面的式子中,向量E所代表的边有内侧和外测之分,将边向量旋转90°(顺时针或者逆时针旋转都可以),便可以构造出该边的法向量,而又因为点F一定是在边的正侧,所以点积Ne.F的符号就是边OE的任一内侧点的符号。因此,如果P点位于该边的内侧的话,那么就必须要满足:
(Ne.F)(Ne.G)=(Ne.(P2-P0))(Ne.(P-P0))≥0
对于任何的点,如果它都位于三角形的三条边的内侧,那么它就在三角形内。从上面的图可以看出,线段P2-P0和法线Ne的点积是大于0(观察其夹角便可知道,其夹角绝对值小于90°),那么线段P-P0和法线Ne的点积也应大于0,即Ne.(P-P0)>0。假定是投影到XY平面上,而Ne又等于P1-P0乘以一个绕Z轴90°的旋转矩阵。令Ne为(NeX,NeY),P0为(x0,y0),P1为(x1,y1),P2为(x2,y2),P为(x,y)则有:
NeX = (x1-x0)*cos90°+(y1-y0)*sin90°
NeY = -(x1-x0)*sin90°+(y1-y0)*cos90°
所以NeX=(y1-y0),NeY=-(x1-x0),求P2在P0P1的那一侧,就求P0P2与法线的夹角值就可以了:当:
Ne.(P2-P0)=NeX*(x2-x1)+NeY*(y2-y1)=(y1-y0)*(x2-x1)+(-(x1-x0)*(y2-y1))>0
就表示p2是在边e的正侧。 而Ne.(P2-P0)=NeX*(x2-x1)+NeY*(y2-y1)经过整理后,实质上就是下面行列式的值,如下:
|x0 y0 1|
|x1 y1 1|
|x2 y2 1|
所以判断点P是否在边e的内侧,就是把上面行列式中点P2的分量代替为点P的分量,只需要计算行列式的值是否大于0便可。大于0,在e的正侧,小于0在e的负侧。下面接着的代码就是根据这个原理实现。
//接上段代码, checkEdgeIntersectsFace函数,tools3d.cpp
float absa = (float)fabs(p_Plane->a);
float absb = (float)fabs(p_Plane->b);
float absc = (float)fabs(p_Plane->c);
static D3DXVECTOR2
face2D[MAX_VERTICES_FOR_EDGE_INTERSECT_CHECKING];
D3DXVECTOR2 point2D;
int i;
//下面的几个if-else判断式,就是根据法线的分量大小,把三角形投影到适当的平面上去。
if ((absa >= absb) && (absa >= absc))
{
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
{
face2D[i].x = p_Face[i].y;
face2D[i].y = p_Face[i].z;
}
point2D.x = p_PointOnPlane->y;
point2D.y = p_PointOnPlane->z;
}
else if ((absb >= absa) && (absb >= absc))
{
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
{
face2D[i].x = p_Face[i].x;
face2D[i].y = p_Face[i].z;
}
point2D.x = p_PointOnPlane->x;
point2D.y = p_PointOnPlane->z;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
{
face2D[i].x = p_Face[i].x;
face2D[i].y = p_Face[i].y;
}
point2D.x = p_PointOnPlane->x;
point2D.y = p_PointOnPlane->y;
}
//p0,p1是多边形的线段的两端点,p2是想要检查的点。
float val;
//这里就是检查(Ne.F)(Ne.G)的结果值
val=(face2D[0].x * face2D[1].y + face2D[0].y * point2D.x
+ face2D[1].x * point2D.y ) -(point2D.x *
face2D[1].y + point2D.y * face2D[0].x +
face2D[1].x * face2D[0].y);
bool cc = val > 0;
bool cctemp;
if (fabs(val) < 0.0001f)
return true; //在边上
//逐个边检查。
for (i = 1; i < numVertices; i++)
{
val = (face2D[i].x * face2D[(i + 1) % numVertices].y
+ face2D[i].y * point2D.x + face2D[(i + 1) %
numVertices].x * point2D.y) -
(point2D.x * face2D[(i + 1) % numVertices].y +
point2D.y * face2D[i].x + face2D[(i + 1) %
numVertices].x * face2D[i].y);
if (fabs(val) < 0.0001f) return true; //在边上
cctemp = val > 0;
if ((cctemp != cc))
{
return false;
}
}
return true; }
10.3.4 分割三角形
void splitTriangle(D3DXPLANE* p_Plane, D3DXVECTOR3* p0,
D3DXVECTOR3* p1, D3DXVECTOR3* p2,
unsigned short* positiveIndices,
DWORD* p_NumPositiveIndices,
unsigned short* negativeIndices,
DWORD* p_NumNegativeIndices)
{
//检查三角形的三个角顶点在分割平面的哪一则?正?负?面上?
int sides[3]; //存储顶点与分割平面的位置信息
int numzero = 0, i;//三角形角顶点在分割平面上的个数
sides[0] = whichSide(p0, p_Plane);
sides[1] = whichSide(p1, p_Plane);
sides[2] = whichSide(p2, p_Plane);
if (sides[0] == 0) numzero++;
if (sides[1] == 0) numzero++;
if (sides[2] == 0) numzero++;
//如果没有角顶点在分割平面上
if (numzero == 0)
{
//检查有多少个角顶点在分割平面的正侧
int numPositive = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (sides[i] == 1) {
numPositive++;
}
}
//根据角顶点在分割平面的正侧的个数,分四种情况考虑。
//情况1:没有一个角顶点在分割平面上,
if (numPositive == 0)
{
//没有一个角顶点在分割平面的正侧,那么所有的角顶点都在
//分割平面的负侧
//在分割平面的正侧的角顶点数为0
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 0;
//在分割平面的负侧的角顶点数为3
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
//记录下在分割平面负侧的角顶点编号
negativeIndices[0] = 0;
negativeIndices[1] = 1;
negativeIndices[2] = 2;
}
//有一个顶点在分割平面的正侧
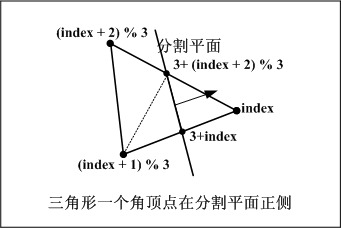
else if (numPositive == 1)
{
// 找到哪个角顶点在分割平面的正侧
int index;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (sides[i] == 1) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
//原三角形在正侧部分被分割成1一个三角形,所以顶点数为3
//在负侧部分被分割成2个三角形,所以顶点数为6
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 6;
positiveIndices[0] = 3 + (index + 2) % 3;
positiveIndices[1] = index;
positiveIndices[2] = 3 + index;
negativeIndices[0] = 3 + index;
negativeIndices[1] = (index + 1) % 3;
negativeIndices[2] = 3 + (index + 2) % 3;
negativeIndices[3] = (index + 1) % 3;
negativeIndices[4] = (index + 2) % 3;
negativeIndices[5] = 3 + (index + 2) % 3;
}
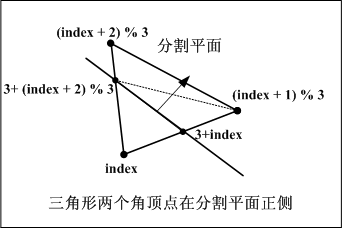
else if (numPositive == 2) {
// 1 point is on negative side
// Find which one is it
int index;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (sides[i] == -1) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
// Two triangles on positive side
// One triangles on negative side
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 6;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
positiveIndices[0] = 3 + index;
positiveIndices[1] = (index + 1) % 3;
positiveIndices[2] = 3 + (index + 2) % 3;
positiveIndices[3] = (index + 1) % 3;
positiveIndices[4] = (index + 2) % 3;
positiveIndices[5] = 3 + (index + 2) % 3;
negativeIndices[0] = 3 + (index + 2) % 3;
negativeIndices[1] = index;
negativeIndices[2] = 3 + index;
} else if (numPositive == 3) {
// Alll points are on positive side
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 0;
positiveIndices[0] = 0;
positiveIndices[1] = 1;
positiveIndices[2] = 2;
}
}

//如果有一个角顶点在分割平面上
else if (numzero == 1) {
//One point is on the plane
//Can either be 1. On one side of the plane
// 2. On two side of the plane
int sum = sides[0] + sides[1] + sides[2];
//-1+1+0=0,一个顶点在分割面正侧,另一个在负侧,一个在面上
if (sum == 0) {
//On two side of the plane
int index;
// Find which one is on the plane
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (sides[i] == 0) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
//分别找到在正侧和在负测的顶点的索引
if (sides[(index + 1) % 3] == 1) {
// Positive
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
positiveIndices[0] = index;
positiveIndices[1] = (index + 1) % 3;
positiveIndices[2] = 3 + (index + 1) % 3;
negativeIndices[0] = 3 + (index + 1) % 3;
negativeIndices[1] = (index + 2) % 3;
negativeIndices[2] = index;
} else {
// Negative
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
positiveIndices[0] = 3 + (index + 1) % 3;
positiveIndices[1] = (index + 2) % 3;
positiveIndices[2] = index;
negativeIndices[0] = index;
negativeIndices[1] = (index + 1) % 3;
negativeIndices[2] = 3 + (index + 1) % 3;
}
}
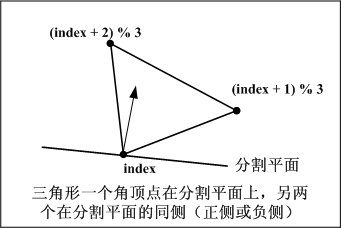
else {
//On one side of the plane
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (sides[i] != 0) {
break;
}
}
if (sides[i] == 1) {
//The triangle is on positive sides
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 0;
positiveIndices[0] = 0;
positiveIndices[1] = 1;
positiveIndices[2] = 2;
} else {
//The triangle is on negative side
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 0;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
negativeIndices[0] = 0;
negativeIndices[1] = 1;
negativeIndices[2] = 2;
}
}
}

else if (numzero == 2) {
//Two points are on the plane
// See which one is not
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (sides[i] != 0) {
break;
}
}
if (sides[i] == 1) {
//The triangle is on positive side
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 0;
positiveIndices[0] = 0;
positiveIndices[1] = 1;
positiveIndices[2] = 2;
} else {
//The triangle is on negative side
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 0;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
negativeIndices[0] = 0;
negativeIndices[1] = 1;
negativeIndices[2] = 2;
}
}
最后一种情况,当被分割的三角形的三个角顶点都在分割平面上,就要检查三角形的法线和分割平面的法线是否同向。同向则表示三角形被分割成一个,在分割平面的正侧;反向则表示三角形也被分割成一个,在分割平面的负侧。
else
{
D3DXVECTOR3 v01, v02, normal;
//利用向量叉积的几何性质,根据三角形的两条边求此三角形的法线。要注意方向
v01 = (*p1) - (*p0);
v02 = (*p2) - (*p0);
D3DXVec3Cross(&normal, &v01, &v02);
D3DXVec3Normalize(&normal, &normal);
//用D3DX库函数计算到平面的的法线。
D3DXPLANE plane = *p_Plane;
D3DXPlaneNormalize(&plane, &plane);
D3DXVECTOR3 planeNormal = D3DXVECTOR3(plane.a, plane.b, plane.c);
//观察两法线的差
D3DXVECTOR3 temp = planeNormal - normal;
//如果两法线的差的模很小很小,接近于0,就可以认为这三角形的
//法线和分割平面的法线是同向。三角形被分在分割平面的正侧,否则
//就分在的负测
if (D3DXVec3Length(&temp) < 0.01f) {
// 在正侧
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 3;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 0;
positiveIndices[0] = 0;
positiveIndices[1] = 1;
positiveIndices[2] = 2;
} else {
// 在负测
*p_NumPositiveIndices = 0;
*p_NumNegativeIndices = 3;
negativeIndices[0] = 0;
negativeIndices[1] = 1;
negativeIndices[2] = 2;
}
}
}
