深度探索DxFramework 10-3
Table of Contents
请尊重原作者的工作,转载时请务必注明转载自:www.xionggf.com
第10章 进入三维的世界 3
10.5 无规矩不成方圆,C_BoundingBox类
10.5.1.包围盒的种类
DXFrameWork的包围盒是一个凸六面体,由6个面,8个顶点,12条边组成的闭合体。因此,DXFrameWork也使用了相关的数据结构来描述包围盒。代码如下:
class C_BoundingBox
{
...
public:
D3DXVECTOR3 point[8]; //8个顶点
D3DXPLANE plane[6]; //6个表面
}
8个顶点和6个面和编号的示意图如下:
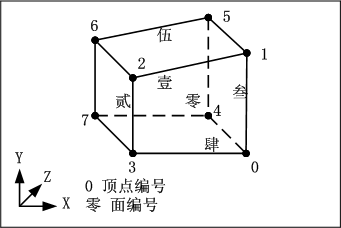
###10.5.2.包围盒的数据结构和初始化设置
//根据给定的图元计算出它的包围盒
void C_BoundingBox::FindBoundingBox(C_Primitive* p_Primitive)
{
unsigned i;
//获取
DWORD numVertices = p_Primitive->numVertices;
// Lock the vertex buffer
C_VertexManipulator vertexMemory;
p_Primitive->LockVertexBuffer(&vertexMemory);
// Find the mins and maxs for each X Y and Z axis
D3DXVECTOR3 position;
float minX;
float minY;
float minZ;
float maxX;
float maxY;
float maxZ;
position = vertexMemory[0].position;
minX = maxX = position.x;
minY = maxY = position.y;
minZ = maxZ = position.z;
//遍历每一个顶点,找出X,Y,Z值最大和最小值
for (i = 1; i < numVertices; i++) {
position = vertexMemory[i].position;
if (position.x < minX) {
minX = position.x;
}
if (position.y < minY) {
minY = position.y;
}
if (position.z < minZ) {
minZ = position.z;
}
if (position.x > maxX) {
maxX = position.x;
}
if (position.y > maxY) {
maxY = position.y;
}
if (position.z > maxZ) {
maxZ = position.z;
}
}
// Unlock the vertex buffer
p_Primitive->UnlockVertexBuffer();
//如果一些图元的包围盒是不是三维的话,比如,一个二维面片的包围盒。
//那么,就要适当地调整一下,使得包围盒能变成三维的
if (fabs(minX - maxX) < 0.01f) {
minX -= 0.1f;
maxX += 0.1f;
}
if (fabs(minY - maxY) < 0.01f) {
minY -= 0.1f;
maxY += 0.1f;
}
if (fabs(minZ - maxZ) < 0.01f) {
minZ -= 0.1f;
maxZ += 0.1f;
}
//创建组成三角形的八个顶点,从0到7的顺序,X,Y,Z值分别是:
//0 右,下,近
//1 右,上,近
//2 左,上,近
//3 右,上,近
//4 右,下,远
//5 右,上,远
//6 左,上,远
//7 左,下,远
// 意思是,前4个
point[0] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, minY, minZ); // Right Bottom Near
point[1] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, maxY, minZ); // Right Top Near
point[2] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, maxY, minZ); // Left Top Near
point[3] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, minY, minZ); // Right Top Near
point[4] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, minY, maxZ); // Right Bottom Far
point[5] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, maxY, maxZ); // Right Top Far
point[6] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, maxY, maxZ); // Left Top Far
point[7] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, minY, maxZ); // Left Bottom Far
// Obtain the 6 plane specifying the bounding box
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[0], &point[2], &point[1], &point[0]); //Near
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[1], &point[5], &point[6], &point[4]); //Far
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[2], &point[7], &point[6], &point[2]); //Left
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[3], &point[1], &point[5], &point[0]); //Right
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[4], &point[4], &point[3], &point[0]); //Bottom
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[5], &point[2], &point[5], &point[1]); //Top
// Validate the bounding box
valid = true;
}
//根据指定的包围盒的大小范围查找到对应的包围盒
void C_BoundingBox::FindBoundingBox(float minX, float minY, float minZ, float maxX, float maxY, float maxZ) {
/* 当有些包围盒不是3D的话,比如其中有一维的值为0,则调整它变成真正三维的盒子*/
if (fabs(minX - maxX) < 0.01f) {
minX -= 0.1f;
maxX += 0.1f;
}
if (fabs(minY - maxY) < 0.01f) {
minY -= 0.1f;
maxY += 0.1f;
}
if (fabs(minZ - maxZ) < 0.01f) {
minZ -= 0.1f;
maxZ += 0.1f;
}
point[0] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, minY, minZ); // Right Bottom Near
point[1] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, maxY, minZ); // Right Top Near
point[2] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, maxY, minZ); // Left Top Near
point[3] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, minY, minZ); // Right Top Near
point[4] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, minY, maxZ); // Right Bottom Far
point[5] = D3DXVECTOR3(maxX, maxY, maxZ); // Right Top Far
point[6] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, maxY, maxZ); // Left Top Far
point[7] = D3DXVECTOR3(minX, minY, maxZ); // Left Bottom Far
// Obtain the 6 plane specifying the bounding box
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[0], &point[2], &point[1], &point[0]); //Near
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[1], &point[5], &point[6], &point[4]); //Far
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[2], &point[7], &point[6], &point[2]); //Left
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[3], &point[1], &point[5], &point[0]); //Right
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[4], &point[4], &point[3], &point[0]); //Bottom
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[5], &point[2], &point[5], &point[1]); //Top
// Validate the bounding box
valid = true;
}
void C_BoundingBox::SetBoundingBox(D3DXVECTOR3 point[8]) { int i;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
this->point[i]=point[i];
}
// Obtain the 6 plane specifying the bounding box
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[0], &point[2], &point[1], &point[0]); //Near
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[1], &point[5], &point[6], &point[4]); //Far
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[2], &point[7], &point[6], &point[2]); //Left
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[3], &point[1], &point[5], &point[0]); //Right
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[4], &point[4], &point[3], &point[0]); //Bottom
D3DXPlaneFromPoints(&plane[5], &point[2], &point[5], &point[1]); //Top
// 确认包围盒有效
valid = true;
}
void C_BoundingBox::SetBoundingBox(D3DXVECTOR3 point[8], D3DXPLANE plane[6])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
this->point[i] = point[i];
}
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
this->plane[i] = plane[i];
}
valid = true;
}
10.5.3.包围盒的相交种类和相交判定
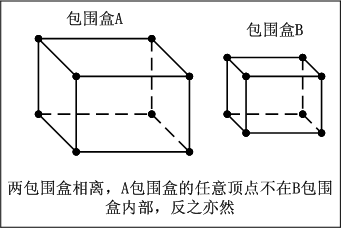
在dxframework中,包围盒的相交种类分为四种,分别是:相离,相交,覆盖,被包含四种。
相离的情况如下,所谓相离是指,A包围盒和B包围盒之间,A包围盒中任意一个顶点,都不在B包围盒内部。或者B包围盒中任意一个顶点,都不在A包围盒的内部。示意图如下:
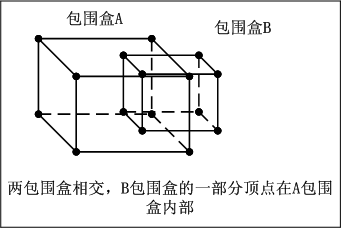
相交是指:B包围盒的一部分的顶点在A包围盒的内部,这时候称为A包围盒与B包围盒相交。示意图如下:
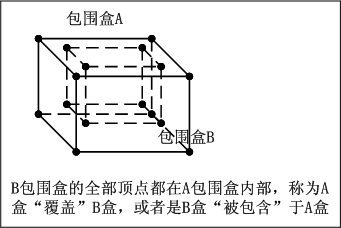
覆盖和被包含是指:B包围盒的全部顶点完全在A包围盒内部。这时候称为A包围盒“覆盖”了B包围盒。或者称为:B包围盒“被包含”于A包围盒。示意图如下:
C_BoundingBox类提供了包围盒相交检测的函数,如下:
//核心函数,判断本包围盒是否和p_BoundingBox包围盒相交
INTERSECTION_TYPE C_BoundingBox::IsIntersecting( C_BoundingBox *p_BoundingBox)
{
if ((p_BoundingBox == NULL) || (!p_BoundingBox->valid) || (!this->valid))
{
//两包围盒必须要有效,即各顶点信息和表明信息要计算好才能进行相交判断
throw Error(_T("C_BoundingBox::IsIntersecting : Bounding box(es) do not exist or are not valid"));
}
//注释约定:first box指本包围盒(this指针所指向的包围盒对象),
//second box指传递进来的参数指针所指向的包围盒。
int i,j;
//out[i]数据中的第k位表示是否第i个包围盒顶点是否在第k个平面的外测
DWORD out[8];
//检查second box的顶点是否在first box里面
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
out[i] = 0;
}
bool aPointInside = false;
int sumOut = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
//调用工具函数,检查第i个second box是否在
//first box的第j个表面正则。
if (positiveSide(&p_BoundingBox->point[i],
&plane[j]))
{
out[i] |=(1 << j);
}
}
//如果第i个second box的顶点都在所有的first box的的负侧
//表明表示这个第i个second box的顶点在first box的内部。
if (!out[i])
{
aPointInside = true;
}
sumOut += out[i];
}
//如果second box至少有一个点在first box的内侧
if (aPointInside)
{
// sumOut等于0。表示所有的second box的顶点都在first box
// 内部。所以first box覆盖second box
if (sumOut == 0)
{
return COMPLETELY_COVER;
}
return PARTIALY_INTERSECTING;
}
D3DXVECTOR3 intersectionPoint;
if ((((((((out[0] & out[1]) & out[2]) & out[3])
& out[4]) & out[5]) & out[6]) & out[7]) != 0)
{
// 所有的顶点都在某一个面的正测,表示这两个包围盒是相离的
return NOT_INTERSECTING;
}
//检查first box的某一边是否穿过second box
{
D3DXVECTOR3 edges[12][2] = {
p_BoundingBox->point[0], p_BoundingBox->point[1],
p_BoundingBox->point[1], p_BoundingBox->point[2],
p_BoundingBox->point[2], p_BoundingBox->point[3],
p_BoundingBox->point[3], p_BoundingBox->point[0],
p_BoundingBox->point[0], p_BoundingBox->point[4],
p_BoundingBox->point[1], p_BoundingBox->point[5],
p_BoundingBox->point[2], p_BoundingBox->point[6],
p_BoundingBox->point[3], p_BoundingBox->point[7],
p_BoundingBox->point[4], p_BoundingBox->point[5],
p_BoundingBox->point[5], p_BoundingBox->point[6],
p_BoundingBox->point[6], p_BoundingBox->point[7],
p_BoundingBox->point[7], p_BoundingBox->point[4]};
D3DXVECTOR3 faces[6][4] = {
point[3], point[2], point[1], point[0],//近Z,XY面
point[5], point[6], point[7], point[4],//远Z,XY面
point[3], point[7], point[6], point[2],//左X,YZ面
point[1], point[5], point[4], point[0],//右X,YZ面
point[4], point[7], point[3], point[0],//底Y,XZ面
point[2], point[6], point[5], point[1]};//顶Y,XZ面
for (i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
//调用工具函数checkEdgeIntersects检查第i条first
//box的边是否穿过第j个second box的面
if(checkEdgeIntersectsFace(edges[i],faces[j],
4, &plane[j], &intersectionPoint))
{
return PARTIALY_INTERSECTING;
}
}
}
}
//检查second box的某一边是否穿过first box
{
D3DXVECTOR3 edges[12][2] = {
point[0], point[1],
point[1], point[2],
point[2], point[3],
point[3], point[0],
point[0], point[4],
point[1], point[5],
point[2], point[6],
point[3], point[7],
point[4], point[5],
point[5], point[6],
point[6], point[7],
point[7], point[4]};
D3DXVECTOR3 faces[6][4] = {
p_BoundingBox->point[3], p_BoundingBox->point[2],
p_BoundingBox->point[1], p_BoundingBox->point[0],
p_BoundingBox->point[5], p_BoundingBox->point[6],
p_BoundingBox->point[7], p_BoundingBox->point[4],
p_BoundingBox->point[3], p_BoundingBox->point[7],
p_BoundingBox->point[6], p_BoundingBox->point[2],
p_BoundingBox->point[1], p_BoundingBox->point[5],
p_BoundingBox->point[4], p_BoundingBox->point[0],
p_BoundingBox->point[4], p_BoundingBox->point[7],
p_BoundingBox->point[3], p_BoundingBox->point[0],
p_BoundingBox->point[2], p_BoundingBox->point[6],
p_BoundingBox->point[5], p_BoundingBox->point[1]};
for (i = 0; i < 12; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
if(checkEdgeIntersectsFace(edges[i],faces[j],
4, &p_BoundingBox->plane[j],
&intersectionPoint))
{
return PARTIALY_INTERSECTING;
}
}
}
}
//检查一下是否first box的一点是否至少在second box的一个面的正侧,
//如果是的话,表示两盒子相离。如果否的话,在上述的各种情况都检查过的
//前提下,就表示,first box在second box的内部,即first box被
//包含于second box
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
if( positiveSide(&point[0],
&p_BoundingBox->plane[i]))
{
return NOT_INTERSECTING;
}
}
return COMPLETELY_INSIDE;
}
上面的函数检查两包围盒相交与否是非常精确的。但是也可以看到,检测的计算非常耗时。尤其是后面判断first box是否被包含于second box的部分。如果我们能够预先知道first box的体积肯定大于second box的话。那么后面的“被包含”判断就可以省略的。因此,DXFrameWork提供了一个比较快速的相交判断函数:INTERSECTION_TYPE C_BoundingBox:: LazyIsIntersecting (C_BoundingBox *p_BoundingBox)。和IsIntersectiong函数相比,LazyIsIntersecting函数省略了检查“被包含”的判断。因此使用此函数的时候,要保证first box的体积大于second box才能得到正确的判断。
除了判断包围盒之间的相交检测之外,C_BoundingBox类还提供了包围盒和线段之间的相交判断函数,如下:
bool C_BoundingBox::IsPenetrated(D3DXVECTOR3 p_Edge[2])
{
int j;
D3DXVECTOR3 intersectionPoint;
D3DXVECTOR3 faces[6][4] = {
point[3], point[2], point[1], point[0], //Near
point[5], point[6], point[7], point[4], //Far
point[3], point[7], point[6], point[2], //Left
point[1], point[5], point[4], point[0], //Right
point[4], point[7], point[3], point[0], //Bottom
point[2], point[6], point[5], point[1]}; //Top
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
if (checkEdgeIntersectsFace(p_Edge, faces[j], 4,&plane[j], &intersectionPoint))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
从上述代码看出,要检查某线段是否和某包围盒相交,就只是需要检查某线段是否和包围盒的任意一个表面相交即可。如果是则表示这线段和包围盒相交,否就表示不相交。
